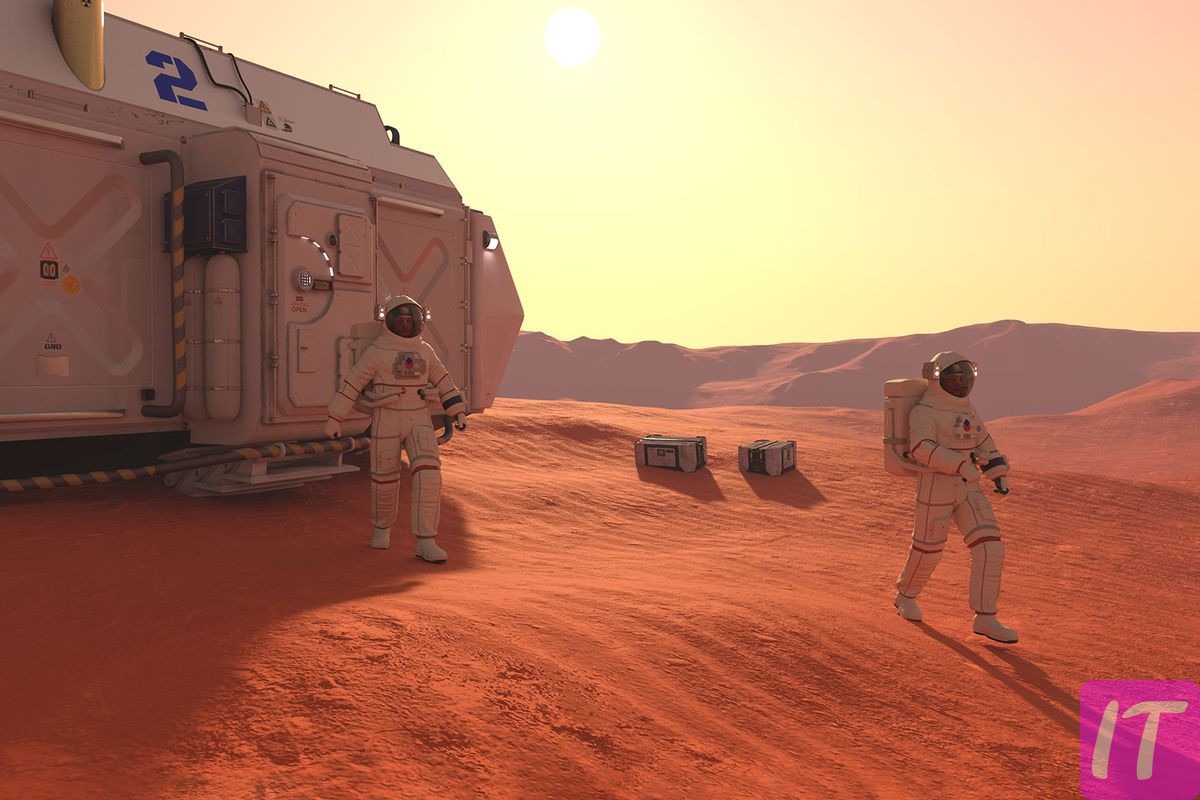
What if the next frontier for human habitation isn’t just across the sea, but beyond Earth’s atmosphere? As scientific advancements escalate, the intriguing idea of living on Mars transitions from pure fiction to potential reality. The Red Planet, with its barren landscapes, poses both immense challenges and tantalizing possibilities for human colonization.
Since NASA’s Viking 1 first landed on Mars in 1976, concepts of Martian habitats have evolved significantly. Modern research focuses on sustainable life support systems, such as using Martian soil for agriculture and extracting water from subterranean ice deposits. Furthermore, SpaceX aims to reduce interplanetary travel costs, making the dream of Martian colonies closer than ever before.

Is there a way for humans to live on Mars?
Living on Mars might sound like science fiction, but it’s a real topic of discussion among scientists. The Red Planet offers some harsh conditions, like freezing temperatures and a thin atmosphere. These challenges need to be solved if humans are to live there. Researchers are investigating how to build habitats that can protect humans. They are also looking into growing food using Martian soil.
One of the main problems with living on Mars is the lack of breathable air. Engineers are working on ways to create oxygen from the carbon dioxide in Mars’ atmosphere. This process, called electrolysis, could be a game-changer. Another big issue is water; without it, humans can’t survive. Scientists think they can extract water from ice found under the Martian surface.
A sustainable way to grow food is crucial for long-term survival on Mars. NASA is experimenting with hydroponics, which involves growing plants without soil. This method could help astronauts produce their own food. Using local resources, such as Martian soil, is also being explored. Successful farming would be a major step towards making Mars livable.
Space agencies like NASA and companies like SpaceX are at the forefront of Mars exploration. SpaceX is planning missions to send humans to Mars within the next decade. NASA’s Perseverance rover is already collecting data that will help future missions. These steps make the vision of living on Mars more realistic. The dream of a Martian colony is closer than ever before.
Examining the Viability of Habitation on Mars
To live on Mars, we must first understand its environment. Mars has a very thin atmosphere composed mostly of carbon dioxide. This atmosphere can’t support human life as it does on Earth. The surface temperature is also extremely cold, averaging around minus 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Such conditions make it essential to develop specialized habitats.
One solution might be building underground or domed habitats to protect from harsh weather and radiation. These structures would provide a controlled environment. Utilizing Martian resources is another key aspect. Technologies for extracting water from ice or generating oxygen from carbon dioxide are crucial. These advancements could make long-term stays possible.
Energy is another critical factor for survival on Mars. Solar panels could provide power, but the dust storms on Mars can block sunlight for weeks. Nuclear energy is another option being explored. Reliable energy sources are necessary for life support systems and daily activities. Energy solutions are still a major area of research.
Finally, the psychological and social aspects of living on Mars can’t be overlooked. Isolation and confinement could pose serious challenges for mental health. Establishing communication with Earth will be important. Virtual reality and other technologies might help people feel connected. Addressing these human factors will be crucial for any successful Mars mission.
Key Challenges of Living on Mars
Living on Mars presents multiple significant challenges. The first major issue is the planet’s extreme temperatures, which range from minus 195 degrees Fahrenheit to 70 degrees Fahrenheit. These freezing temperatures make it difficult for humans to survive without advanced heating systems. Another crucial problem is the thin Martian atmosphere. This atmosphere provides little protection from harmful solar radiation.
Another challenge is the lack of liquid water. While there is ice on Mars, accessing and melting it for use poses a technical challenge. Without water, humans can’t grow food or stay hydrated. Transporting enough water from Earth is impractical. Innovations in water extraction technologies are vital for addressing this issue.
Energy production also remains a difficult hurdle. Mars lacks a consistent energy source like Earth’s fossil fuels. Solar energy could be an option, but dust storms on Mars can last for weeks, blocking sunlight. Nuclear power is being considered as a possible alternative. Reliable energy is needed for heating, oxygen production, and daily activities.
Lastly, the psychological challenges of living on Mars should not be ignored. The isolation and confinement in a small habitat could affect mental health. Communication delays with Earth add another layer of difficulty. Support systems and leisure activities will be important. Addressing these human factors will be crucial to any Mars mission.
Potential Technological Solutions for Martian Colonization
To support human life on Mars, scientists are developing advanced technologies. One critical area is life support systems, which include methods to produce oxygen and water. NASA is testing equipment like the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) to convert Martian carbon dioxide into breathable oxygen. Finding water involves using robotics to extract ice from beneath the surface. These technologies can significantly reduce the need for supplies from Earth.
Another focus is on building sustainable habitats. Martian habitats must protect humans from the harsh environment, including extreme temperatures and radiation. Engineers are designing structures using materials found on Mars, like regolith. 3D printing is also being explored to create robust buildings. These methods could eventually lead to self-sustaining colonies.
Food production is another major challenge that technology can solve. Hydroponics and aeroponics systems allow plants to grow without soil, using nutrient-rich water or air. Scientists are testing these systems in space conditions to ensure they can work on Mars. Successful food production will make colonies less reliant on Earth. This also offers psychological benefits, giving colonists fresher, varied diets.
Energy production is crucial for maintaining life on Mars. Solar panels are an obvious choice but are not always reliable due to dust storms. Nuclear reactors provide an alternative, offering a steady energy source. NASA is working on small, portable reactors for this purpose. Consistent energy ensures that all life-supporting systems function properly.
Transportation and mobility on Mars also require innovation. Rovers and drones can help with exploration and resource collection. Space agencies are developing vehicles designed to operate in Mars’ low gravity and thin atmosphere. These machines can perform tasks that would be difficult or dangerous for humans. Enhanced mobility will allow for more comprehensive exploration and faster setup of colonies.
The Role of SpaceX and NASA in Mars Exploration
SpaceX and NASA are at the forefront of Mars exploration. SpaceX, led by Elon Musk, has ambitious plans to colonize Mars. The company’s Starship rocket is designed to carry humans and cargo to the Red Planet. Frequent test flights are paving the way for future missions. SpaceX aims to make interplanetary travel affordable and accessible.
NASA plays a crucial role in understanding Mars through its various missions. The Perseverance rover, which landed in 2021, is collecting samples and studying the Martian environment. NASA’s InSight mission is also providing valuable data on Mars’ geology. These missions lay the groundwork for human exploration. Information gathered helps scientists develop technology for future manned missions.
Partnerships between NASA and SpaceX are essential for advancements. For example, NASA has contracted SpaceX to develop the Human Landing System for the Artemis program. This program aims to return humans to the Moon as a practice run for Mars. Both agencies benefit from shared knowledge and resources. Collaboration speeds up the development process.
SpaceX focuses on rocket technology and transportation. Their goal is to build a fleet of Starships capable of carrying people to Mars. The company is also working on systems to produce fuel on Mars using local resources. This approach would make return trips more feasible. Technological advances in these areas are vital for long-term colonization.
NASA invests in scientific research and life support systems. They are testing methods to produce oxygen and grow food on Mars. The agency also works on space habitats and human health. These projects are crucial for sustaining human life. NASA’s expertise is indispensable for making sure humans can live on Mars safely.
Both SpaceX and NASA aim to make human life multi-planetary. Their combined efforts are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As technology advances, trips to Mars will become more routine. The work done by these organizations is bringing the dream of living on Mars closer to reality.

Frequently Asked Questions
Curious about living on Mars? Here are some common questions and answers that delve deeper into the possibilities and challenges of life on the Red Planet.
1. How long would a journey to Mars take?
A journey to Mars would typically take about 6 to 9 months, depending on the alignment of Earth and Mars. The distance between the two planets varies due to their elliptical orbits, making timing crucial for space missions.
During this trip, astronauts would need to navigate radiation exposure and limited supplies. Scientists are actively researching ways to make space travel safer and more efficient for such long-duration missions.
2. What are the primary sources of energy proposed for Martian colonies?
The primary sources of energy for Martian colonies include solar power and nuclear reactors. Solar panels can capture sunlight, but dust storms may reduce their efficiency. Therefore, reliable backup systems are necessary.
Nuclear reactors offer consistent energy production regardless of weather conditions. They could provide a stable source of electricity for habitats, life support systems, and research equipment on Mars.
3: Can humans grow food on Mars?
Yes, humans can grow food on Mars using methods like hydroponics and aeroponics. These techniques allow plants to grow without soil by providing nutrients through water or air mist.
NASA is experimenting with these systems to ensure sustainability in future missions. Growing food locally reduces dependence on supply shipments from Earth, making long-term colonization more feasible.
4: What role does SpaceX play in Mars exploration?
SpaceX aims to make Mars colonization a reality through its ambitious projects like the Starship rocket. The company’s goal is to transport humans and cargo to Mars affordably.
This includes developing technologies for fuel production on Mars using local resources. SpaceX’s work complements NASA’s efforts by focusing on transportation solutions crucial for sustained human presence on the Red Planet.
5: Are there any health risks associated with living on Mars?
Living on Mars poses several health risks including exposure to higher levels of radiation compared to Earth. The thin Martian atmosphere provides little protection from cosmic rays and solar radiation, leading to potential long-term health issues.
Poor gravity conditions might also impact astronauts’ muscle mass and bone density over time. Continuous research aims to develop countermeasures like protective habitats and exercise regimes tailored for space environments.
Conclusion
The prospect of living on Mars is not only fascinating but also achievable with continued technological innovation and research. SpaceX and NASA are making significant strides, focusing on transportation, energy, and life support systems. Overcoming Mars’ harsh environment will require international collaboration and sustained effort.
Advancements in habitat construction, renewable energy, and sustainable farming bring us closer to making Mars a second home. While challenges remain, the combined efforts of governments and private companies offer hope. The dream of establishing a human colony on Mars is more tangible than ever before.