ITEACH.TOP | LEARN EVERYTHING
What is the Dark Web and What Do You Know About It?
Understanding the intricacies of the internet reveals layers that are often invisible to the average user. One of these layers is the dark web, a shadowy part of the internet often shrouded in mystery and intrigue.
Understanding the Basics of the Dark Web
The dark web is a subset of the deep web, marked by sites that conduct illicit activities hidden from the prying eyes of traditional search engines. Unlike the surface web, which is accessible to anyone with an internet connection and a browser, the dark web requires specific software and configurations to access. One commonly used tool is Tor (The Onion Router), designed to anonymize users and conceal their activities. Not all activities on the dark web are illegal, but its anonymity often attracts criminal elements.
A significant portion of the dark web’s content includes private forums, black markets, and other hubs for illegal trade. These markets often deal in drugs, firearms, stolen personal data, and more. The dark web functions within an encrypted network, where users often employ cryptocurrencies to complete transactions, providing both parties with anonymity.
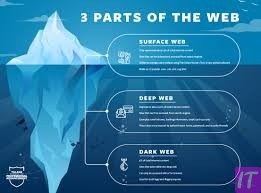
Understanding the differences between the surface web, deep web, and dark web is crucial for anyone studying this layered structure. The surface web is indexed by search engines like Google and is accessible to the general public. In contrast, the deep web includes vast amounts of private data like academic records, email accounts, and proprietary databases (content that is not indexed by search engines but is not inherently illicit).
The Difference Between the Surface Web, Deep Web, and Dark Web
The surface web is the portion of the internet that the average user can access without special tools. It’s where websites are indexed by search engines for easy discovery. This includes everything from Wikipedia to news articles. In contrast, the deep web encompasses vast amounts of data not indexed by search engines, such as academic databases, private company intranets, and personal email accounts.
The dark web is a distinct part of this unindexed content but requires specific software to access. While the deep web simply includes pages not accessible via standard search engines, the dark web is intentionally hidden and often involves more complex access protocols. For instance, the dark web is predominantly accessed through Tor, which anonymizes user activity.
The size of each segment varies significantly. The surface web is only a small fraction of the entire internet, whereas the deep web is massively larger. The dark web is an even smaller subset of the deep web, but it garners significant attention due to its association with illegal activities.
Despite its reputation, the dark web also hosts some legitimate and legal content, such as privacy-focused services and communications platforms used by whistleblowers and journalists. This duality underscores the multifaceted nature of the dark web.
How Does the Dark Web Operate?
The dark web operates through a series of complex networks that prioritize user privacy and anonymity. Tor is the most widely known tool for accessing the dark web. Tor routes internet traffic through a series of nodes to obscure user IP addresses, making tracking difficult. This structure creates a layered encryption system, hence the term “onion routing.”
Websites on the dark web often have addresses ending in “.onion” rather than more familiar domains like “.com” or “.org.” These sites are not indexed by traditional search engines, making navigation akin to knowing coordinates in a mapless landscape.
Transactions within the dark web frequently use cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Monero. These digital currencies offer a higher level of anonymity compared to traditional banking systems, which is crucial for many users on the dark web.
Communication within this realm often relies on encrypted messaging services. Encryption tools help maintain privacy, ensuring that only intended recipients can read messages. This is critical for both legal users focused on privacy and illegal operators protecting their activities.
Key Terminology Associated with the Dark Web
To understand the dark web, it’s essential to familiarize oneself with specific terminologies. “Tor” refers to The Onion Router, a prevalent method to access the dark web, providing anonymity through multi-layered encryption. Another term, “Onion address,” signifies the unique address ending in “.onion” used by sites on the dark web.
“Cryptocurrency” is frequently mentioned in dark web discussions, primarily because it ensures transaction anonymity. Common cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin and Monero. “Encryption” is another vital term, referring to the method of converting data into a secure code to prevent unauthorized access.
“P2P (peer-to-peer) networks” describe decentralized networks where participants share resources directly without a central server. “Marketplace” often pertains to sites on the dark web selling illegal goods. Understanding these and other terms is fundamental to grasp the dark web’s operations effectively.
Myths and Facts About the Dark Web
There are many myths surrounding the dark web. One common myth is that the dark web is exclusively used for illegal activities. While illegal activities do occur, the dark web also hosts legitimate uses, such as secure communication channels for journalists and activists.
Another myth is that accessing the dark web is illegal. Accessing the dark web itself is not illegal, but engaging in unlawful activities there is. It is essential to distinguish between the legality of access versus the illegality of activities conducted on it.
A prevalent myth is the ease of accessing and navigating the dark web. In reality, accessing the dark web requires specific software like Tor and knowledge of where to find .onion links, which are not indexed by search engines.
Navigating the Dark Web: Is It Legal?
Navigating the dark web itself is not inherently illegal. However, what one does on the dark web can cross legal boundaries. For instance, buying or selling illegal substances, weapons, or stolen data is illegal and can lead to severe consequences.
Many countries have laws that make it legal to access the dark web but illegal to participate in criminal activities on it. This means that browsing is permissible, but engaging in illicit transactions is not.
Legal uses of the dark web include anonymous browsing, protecting privacy, and conducting research. It’s crucial for users to be aware of their national and local laws concerning the dark web to avoid inadvertent legal issues.
The Role of Tor in the Dark Web Ecosystem
Tor plays a crucial role in the dark web ecosystem by enabling anonymous browsing and communication. It does this by routing internet traffic through a series of volunteer-operated nodes around the world, obscuring users’ locations and usage patterns.
Tor’s layered encryption (akin to layers of an onion) ensures that each node only knows the location of the previous and next nodes, making it extremely difficult to trace the entire path back to the user. This anonymity is a double-edged sword, offering privacy for legitimate uses and shield for illegal activities.
Servers hosting dark web content also use Tor, ensuring that their locations remain undisclosed. This decentralized approach makes it challenging for authorities to take down illegal sites, contributing to the dark web’s resilience.
Dark Web Marketplaces: A Closer Look
Dark web marketplaces function similarly to e-commerce platforms like eBay or Amazon but operate within the illegal domain. These marketplaces sell a variety of goods and services, ranging from counterfeit currencies to stolen credit card information and illegal drugs.
The marketplaces often use escrow services to build trust between buyers and sellers. Once the buyer confirms the receipt of goods, the payment (usually in cryptocurrency) is released to the seller. This helps mitigate the risk for buyers and sellers involved in illegal transactions.
Marketplaces frequently get disrupted and subject to law enforcement crackdowns. However, the decentralized and anonymous nature of the dark web facilitates the emergence of new marketplaces, perpetuating the cycle of illegal trade.
Illegal Activities Commonly Found on the Dark Web
Illegal activities are rampant on the dark web. The primary ones include the sale of narcotics, firearms, and counterfeit goods. Stolen data, including credit card numbers, social security numbers, and login credentials, is also commonly traded.
Cybercriminal services, such as hacking for hire and malware distribution, find a thriving market on the dark web. These activities exploit the anonymity and decentralized nature of the dark web to operate with relative impunity.
Human trafficking and illegal pornography are other heinous activities facilitated by dark web networks. Law enforcement agencies continuously strive to combat these activities, albeit with varying degrees of success.

Cybersecurity Threats Emerging from the Dark Web
The dark web is a fertile ground for cybersecurity threats. Cybercriminals use it to distribute malware, ransomware, and other malicious software. These attacks often target unprotected or poorly secured systems, causing significant damage.
Phishing kits and tools for conducting DDoS attacks are readily available on dark web marketplaces. These tools enable less technically skilled individuals to carry out sophisticated cyberattacks, increasing the overall threat landscape.
Organizations must remain vigilant and employ advanced cybersecurity measures to mitigate these threats. Regular security audits, employee training, and robust incident response strategies are essential to defend against dark web-sourced cybersecurity threats.
The Effectiveness of Law Enforcement on the Dark Web
Law enforcement agencies face substantial challenges in combating dark web activities. The anonymity and encryption provided by networks like Tor make it difficult to trace users and dismantle illegal operations.
International collaboration is often required, as dark web activities transcend national borders. Agencies like Europol and the FBI have conducted successful operations to shut down major dark web marketplaces, such as Silk Road and AlphaBay.
Despite these successes, the dark web’s decentralized and resilient structure ensures that new illegal marketplaces quickly emerge. Continuous efforts and innovative approaches are necessary for law enforcement to stay ahead.
Privacy and Anonymity: The Double-Edged Sword
Privacy and anonymity are the core tenets of the dark web, offering protection for both legal and illegal activities. Whistleblowers, journalists, and activists use the dark web to communicate privately and securely, safeguarding themselves from repressive regimes and threats.
Conversely, the same anonymity provides a haven for criminal activities. The difficulty of tracing users and transactions complicates law enforcement efforts to curb illegal activities.
Balancing privacy and security is a delicate task. While anonymity can protect individual freedoms, it can also facilitate crime, necessitating careful consideration of policy and technological solutions.
Ethical Considerations When Exploring the Dark Web
Exploring the dark web raises several ethical considerations. Researchers, journalists, and security professionals often need to navigate the dark web to gather information, posing ethical dilemmas regarding exposure to illegal content.
Responsible usage requires a thorough understanding of the legal and ethical boundaries. One must avoid participating in, or inadvertently supporting, illegal activities while conducting legitimate research or investigations.
Educational institutions and organizations should provide guidelines and training to ensure ethical conduct when exploring the dark web. This ensures that users are aware of the potential risks and ethical implications.
How Hackers Exploit the Dark Web
Hackers exploit the dark web to sell stolen data and hacking tools. Breached data, including personal information and financial details, is often traded on dark web forums, contributing to identity theft and financial fraud.
Exploits and vulnerabilities are shared among cybercriminals, who use this information to develop and deploy attacks. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is another prevalent model, allowing individuals to launch ransomware attacks without extensive technical knowledge.
Organizations must prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect against such threats. Understanding hacker methodologies and maintaining updated security protocols can significantly reduce the risk of exploitation.
The Evolution of the Dark Web Over the Years
The dark web has evolved considerably since its inception. Initially, it was a niche area for tech enthusiasts and privacy advocates. Over time, it expanded to include a wide range of activities including illegal trade.
The shutdown of major marketplaces like Silk Road marked significant milestones, yet the dark web’s resilient nature ensured its continuity. New marketplaces arose, incorporating advanced security measures and decentralized models to avoid detection.
Technological advancements and increasing scrutiny from law enforcement have shaped the dark web’s evolution. The continuous cat-and-mouse game between authorities and cybercriminals will undoubtedly drive further changes.
Opportunities and Risks for Businesses on the Dark Web
Businesses face both opportunities and risks concerning the dark web. Cybersecurity firms, for instance, monitor dark web activities to identify emerging threats and protect their clients’ vulnerabilities.
Conversely, businesses are at risk of having their data and intellectual property stolen and sold on the dark web. This necessitates robust cybersecurity practices and proactive monitoring to mitigate potential threats.
Understanding the dark web’s landscape can help organizations develop effective strategies to protect their assets. Leveraging dark web intelligence can significantly enhance a company’s security posture.
Understanding Cryptocurrency’s Role in Dark Web Transactions
Cryptocurrencies play a pivotal role in dark web transactions. Bitcoin was one of the first cryptocurrencies widely adopted for its pseudonymous nature, allowing users to conduct transactions without revealing their identities fully.
Monero has gained popularity due to its enhanced privacy features, making transactions even more difficult to trace. These cryptocurrencies provide a level of anonymity conducive to the dark web’s ecosystem.
Law enforcement agencies have developed tools to track cryptocurrency transactions, though these efforts face limitations. The ongoing evolution of privacy-centric cryptocurrencies continues to present challenges.
So You Want to Visit the Dark Web: Tips and Warnings
If you plan to visit the dark web, it’s crucial to proceed with caution. Use reputed software like Tor to ensure secure access and employ comprehensive security measures such as updated antivirus software and firewalls.
Avoid engaging in any illegal activities or visiting questionable sites. Even inadvertent exposure to illegal content can have serious repercussions. Stick to legitimate and known addresses if there’s a valid reason for your visit.
Always cover your tracks and consider using additional anonymity tools like VPNs. Understand the legal implications and conduct thorough research before accessing the dark web to stay on the right side of the law.

Impact of Dark Web Activities on Modern Society
The dark web’s activities significantly impact modern society. On one hand, it allows for privacy and freedom of expression in repressive environments. On the other, it facilitates illegal trade, cybercrime, and other nefarious activities.
The sale of stolen data on the dark web contributes to identity theft and financial fraud, affecting individuals and organizations alike. The distribution of illegal drugs and firearms poses societal risks, contributing to crime and substance abuse issues.
Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of the dark web remains a complex challenge. Society must find ways to leverage the dark web’s positive aspects while mitigating its threats.
Future Trends and Predictions for the Dark Web
The dark web is expected to continue evolving with technological advancements and increasing regulatory scrutiny. The development of new privacy-centric tools will likely enhance anonymity, making law enforcement efforts more challenging.
Cryptocurrencies will remain integral, with newer coins offering more robust privacy features. The rise of decentralized marketplaces may further complicate the task of shutting down illegal operations.
Law enforcement agencies will need to innovate and collaborate globally to address these challenges effectively. Public awareness and education about dark web risks and cyber hygiene will also play a crucial role in shaping the future landscape.
Conclusion
The dark web is a complex and multifaceted part of the internet, encompassing both positive uses and significant risks. Understanding its structure, operations, and the distinctions between the surface web, deep web, and dark web is crucial for anyone delving into this hidden realm. While privacy and anonymity provide valuable protections, they also enable various illegal activities, presenting ongoing challenges for law enforcement, businesses, and individuals. By staying informed and cautious, users can navigate the dark web’s complexities responsibly and ethically. As technology and regulations evolve, so will the strategies to leverage and mitigate the dark web’s impact on modern society.







